The global push for energy efficiency and sustainability has significantly transformed the electric motor industry. Motors consume nearly half of the world’s electricity, making energy-efficient designs critical for industrial operations, transportation systems, and household appliances. Energy-saving motors, compliant with stringent international standards such as IE3 and IE4, are increasingly demanded in sectors ranging from manufacturing and HVAC to electric vehicles.
A critical element in these motors is the laminated steel core, commonly referred to as motor laminations. These thin, durable laminations reduce energy losses associated with eddy currents and hysteresis, thereby improving motor efficiency. With global energy regulations tightening and companies aiming to reduce operational costs, the demand for high-performance motor laminations has grown significantly. Manufacturers are focusing on materials and processes that provide both superior electrical performance and mechanical durability.
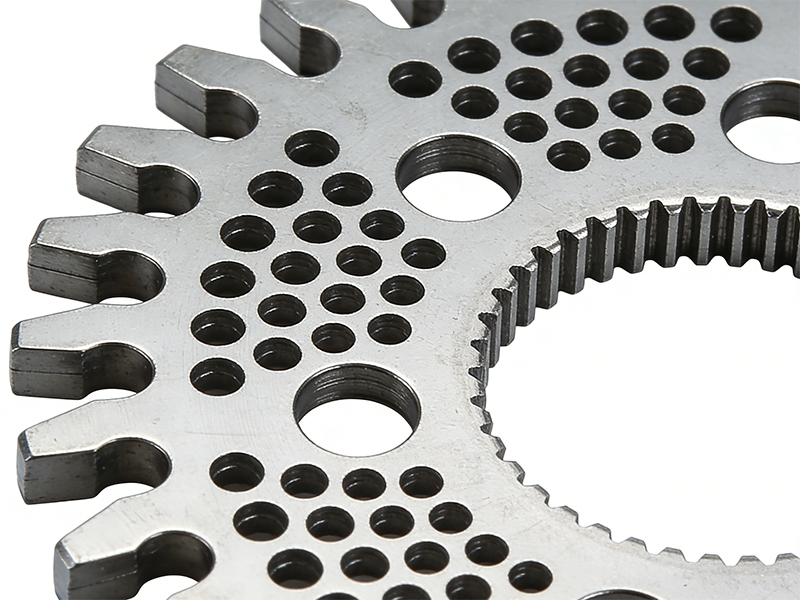
Motor laminations are essentially thin sheets of electrical steel stacked to form the stator and rotor cores of an electric motor. The primary function of these laminations is to provide a low-loss magnetic path for the alternating magnetic fields in the motor while minimizing energy losses caused by eddy currents.
Two key concepts govern their performance:
Magnetic Properties: High-permeability electrical steel allows efficient magnetic flux conduction. The choice between grain-oriented and non-grain-oriented steels depends on motor type; grain-oriented steels are typically used in transformers, while non-grain-oriented steels are preferred for rotating machines.
Lamination Thickness: Thinner laminations reduce eddy current losses but increase manufacturing complexity and cost. Optimal thickness balances electrical efficiency with structural integrity.
Advances in material science have led to improved silicon steel compositions and surface insulation coatings. These innovations enhance magnetic performance while maintaining mechanical strength, which is crucial for high-speed or high-torque motors.
Motor laminations are designed as precise, thin sheets with intricate geometries, often featuring slots, notches, or teeth to accommodate windings and facilitate magnetic flux. The uniform stacking of these laminations forms the stator and rotor cores. Proper alignment and stacking techniques are essential to minimize air gaps and maintain consistent magnetic paths.
High-quality electrical steel forms the backbone of efficient motor laminations. Silicon content is carefully controlled (typically 2–3%) to reduce hysteresis losses, while alloying elements improve tensile strength and machinability. Additionally, surface coatings, such as phosphate or oxide layers, provide electrical insulation between sheets to prevent eddy currents. These coatings must withstand high temperatures, mechanical stress, and exposure to humidity or chemicals during operation.
The production of thin motor laminations involves several critical steps:
Cold Rolling: Electrical steel is rolled to precise thicknesses, often below 0.35 mm for modern high-efficiency motors. Cold rolling ensures uniform thickness and enhances material strength.
Annealing: Heat treatment relieves internal stresses, improves magnetic properties, and prepares the steel for stamping or laser cutting.
Cutting or Stamping: Advanced laser or mechanical stamping techniques create complex shapes while maintaining tight tolerances. High-precision cutting reduces burrs and deformations that could compromise performance.
Insulating Coating Application: Each lamination receives an insulating coating to electrically separate layers in the stacked core. Uniformity and adhesion are critical for long-term reliability.
Stacking and Core Assembly: Laminations are stacked using mechanical presses, bonding agents, or welding in some designs. Proper alignment prevents magnetic leakage and ensures consistent performance.
Thin and durable motor laminations provide several performance benefits:
Reduced Energy Loss: Thinner laminations lower eddy current losses, improving overall motor efficiency.
Enhanced Thermal Management: Efficient magnetic cores generate less heat, reducing cooling requirements.
Mechanical Durability: High tensile strength and precise assembly reduce vibration and noise.
Longevity: Stable coatings and robust materials extend service life under cyclic loading.
Motor laminations’ performance is highly sensitive to multiple factors:
Material Consistency: Variations in silicon content or alloying elements can significantly alter magnetic properties.
Lamination Thickness Precision: Deviations can increase eddy current losses and reduce efficiency.
Insulation Quality: Poor coatings can lead to short-circuited laminations, increasing heat and reducing motor lifespan.
Stacking Accuracy: Misalignment or uneven stacking creates gaps in the magnetic circuit, increasing losses and mechanical stress.
Surface Finish: Burrs, scratches, or deformations from cutting processes degrade magnetic performance and can cause noise or vibration.
Strict quality control during each manufacturing step is essential to maintain optimal performance, especially for high-speed, high-efficiency motors where tolerances are exceptionally tight.
For OEMs and motor manufacturers, sourcing reliable motor laminations is critical. Key criteria for selecting suppliers include:
Material Certification: Compliance with international standards (IEC, ASTM) ensures electrical steel meets magnetic and mechanical specifications.
Manufacturing Capability: Suppliers must offer advanced rolling, stamping, coating, and annealing capabilities to produce thin, precise laminations.
Consistency and Yield: High yield rates reduce scrap and maintain cost efficiency.
Technical Support: Suppliers offering design assistance and testing services help optimize laminations for specific motor applications.
Logistics and Delivery: Timely delivery of large-volume orders is crucial for uninterrupted motor production schedules.
Choosing suppliers with proven experience in energy-efficient motors reduces risk and ensures consistent quality, especially for applications in automotive, industrial, and renewable energy sectors.
Despite technological advances, several challenges persist:
Balancing Thinness and Durability: Ultra-thin laminations improve efficiency but can be fragile during handling or stacking.
Cost vs. Performance: High-grade silicon steel and precision coatings increase material costs. Manufacturers must balance efficiency gains against overall motor cost.
Thermal and Mechanical Stress: Motors operating in harsh environments, such as electric vehicles or industrial machinery, place laminations under repeated thermal cycling and vibration.
Supply Chain Reliability: Limited suppliers for high-quality laminations can create bottlenecks, especially during peak demand periods.
Addressing these issues requires a combination of material innovation, precise manufacturing, and rigorous quality assurance.
Thin and durable motor laminations are integral to numerous energy-saving applications:
Industrial Motors: In pumps, compressors, and conveyors, high-efficiency motors reduce operational energy costs. Laminations minimize magnetic losses and heat generation during continuous operation.
HVAC Systems: Energy-efficient fans and compressors in heating and cooling systems rely on optimized laminations to meet stringent energy regulations.
Electric Vehicles: Automotive motors demand lightweight, high-efficiency laminations to maximize range and performance while withstanding high rotational speeds and torque.
Renewable Energy: Wind turbines and hydroelectric generators benefit from low-loss laminations that enhance energy conversion efficiency and reliability.
Home Appliances: High-performance motors in washing machines, refrigerators, and air conditioners improve energy efficiency and reduce noise.
In each scenario, lamination quality directly impacts energy consumption, reliability, and operational cost, making them a critical component in energy-saving motor design.
The motor industry is rapidly evolving under energy efficiency and electrification trends. Key developments in motor laminations include:
Ultra-Thin Laminations: Advancements in rolling and coating technologies allow for laminations as thin as 0.20 mm, significantly reducing eddy current losses.
Amorphous and Nanocrystalline Materials: Emerging materials with near-zero hysteresis losses are being explored for high-performance applications, particularly in variable-speed motors.
Integrated Design Tools: Simulation software enables precise modeling of magnetic flux, thermal behavior, and mechanical stresses, optimizing lamination design before production.
Sustainable Materials and Processes: Manufacturers are focusing on eco-friendly steel production and low-emission coating processes to meet environmental regulations.
High-Speed Motor Applications: Electric aircraft, drones, and EV traction motors drive demand for laminations with higher tensile strength and thermal stability.
As global energy policies tighten and demand for electric propulsion grows, motor laminations will continue to evolve toward thinner, stronger, and more efficient designs.
Q1: Why are motor laminations important for energy efficiency?
Motor laminations reduce eddy current and hysteresis losses in the core, lowering energy consumption and heat generation, which directly improves motor efficiency.
Q2: What materials are commonly used for motor laminations?
Non-grain-oriented silicon steel with 2–3% silicon content is the most common. Surface coatings such as phosphate or oxide layers provide electrical insulation between laminations.
Q3: How does lamination thickness affect motor performance?
Thinner laminations reduce eddy current losses, enhancing efficiency, but may increase manufacturing complexity and cost. Optimal thickness balances performance and durability.
Q4: What are common manufacturing challenges for thin laminations?
Maintaining uniform thickness, avoiding burrs during cutting, ensuring precise stacking, and applying durable insulation coatings are critical challenges.
Q5: Which industries benefit most from energy-saving motor laminations?
Industrial manufacturing, HVAC, automotive, renewable energy, and household appliances all benefit from improved efficiency and reduced operational costs.
Thin and durable motor laminations are fundamental to energy-saving motors, directly influencing efficiency, heat management, mechanical reliability, and operational lifespan. With increasing global emphasis on energy efficiency and sustainability, high-quality laminations are essential for modern motor designs across industrial, automotive, and renewable energy applications.
The future of motor laminations is set to emphasize ultra-thin designs, advanced materials, and sustainable manufacturing processes. Companies investing in precise, high-performance laminations gain a competitive advantage by delivering motors that meet regulatory standards, reduce energy consumption, and perform reliably in demanding environments.
By understanding the material science, manufacturing processes, and application requirements, motor designers and manufacturers can optimize laminations to achieve both technical performance and economic benefits, ensuring energy-efficient solutions for a wide range of industries.

Авторское право © Чжэцзянская компания электромеханических технологий Синьчжэн. Все права защищены.
Этот веб-сайт использует файлы cookie, чтобы обеспечить вам максимально эффективное использование нашего веб-сайта.